Map reveals states with rising cancer rates
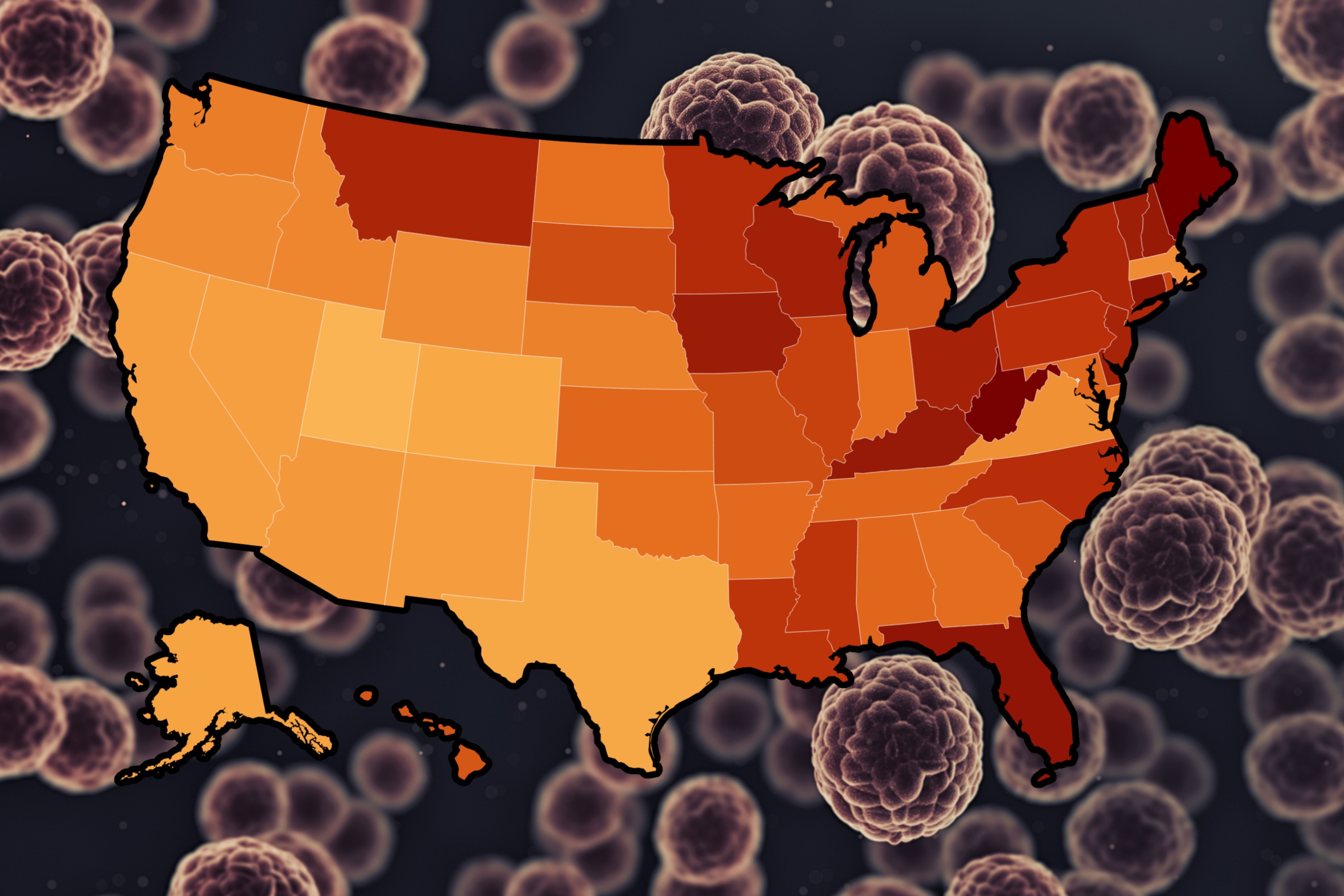
Cancer Diagnosis Rates Vary Widely Across the United States
Cancer diagnosis rates vary significantly across different regions of the United States, with some areas reporting much higher rates than others. A recent analysis of data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has revealed these disparities, highlighting how cancer incidence can differ dramatically depending on where people live.
Maine Leads in Cancer Diagnoses
Maine has the highest cancer diagnosis rate in the country, with 650 cases per 100,000 residents in 2021. This is the highest rate recorded among all U.S. states. The most common types of cancer in Maine are breast cancer, followed closely by lung and bronchus cancers. These findings suggest that certain risk factors or environmental conditions may be contributing to the high incidence of cancer in this region.
In contrast, Utah has the lowest cancer rate nationwide, with only 358 cases per 100,000 residents. This figure is 45% lower than Maine’s, indicating a significant regional difference in cancer prevalence. Unlike national trends, prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed form in Utah, while lung cancer ranks fifth. This variation highlights the importance of understanding local health patterns and risk factors.
Regional Disparities in Cancer Incidence
The analysis also revealed a clear divide between the East and West coasts in terms of cancer diagnosis rates. The Northeast and Appalachian regions have the highest cancer rates, with several states ranking among the top in the nation. For example:
- West Virginia reported 643 cases per 100,000 residents.
- Kentucky had 583 cases per 100,000 residents.
- Florida and Connecticut both ranked high, with 596 and 592 cases respectively.
- New Hampshire rounded out the top five with 582 cases per 100,000 residents.
These states share similar characteristics, including high rates of lung and bronchus cancers, which may be linked to factors such as smoking, environmental exposure, or limited access to healthcare.
On the other hand, Western and Southwestern states generally report much lower cancer incidence. For instance:
- Colorado had 389 cases per 100,000 residents.
- Texas reported 392 cases.
- Nevada had 413 cases.
In most of these lower-incidence states, breast cancer remains the most common type, except in Utah, where prostate cancer is the leading diagnosis.
Social and Economic Factors Influence Cancer Rates
Dr. Robert Winn, Director and Lipman Chair in Oncology at the VCU Massey Comprehensive Cancer Center, explained that differences in cancer rates could reflect broader social and economic disparities. He pointed to the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Cancer Disparities Progress Report, which emphasizes the impact of social determinants on health outcomes.
"Social, economic, and physical conditions in the places where people live, work, and play can affect their health," Dr. Winn said. "Factors such as socioeconomic status, housing, transportation, access to healthy food, clean air and water, and healthcare services all play a role in cancer risk and outcomes."
Should People in High-Risk Areas Be Concerned?
While the high cancer diagnosis rates in certain regions are concerning, experts emphasize that early detection and prevention can make a significant difference. Dr. Winn noted that many people living in rural areas face challenges in accessing timely care, which can contribute to higher diagnosis rates.
"There is definitely a concern that more people are being diagnosed with cancer, especially in rural areas," he said. "That's why it's critical to identify and eliminate risk factors, screen early, and prevent cancer from spreading."
However, he also stressed that a cancer diagnosis does not always mean a death sentence. Over the past three decades, advancements in research, treatment, and early detection have led to a significant decline in cancer mortality.
A Positive Trend in Cancer Survival
According to Dr. Winn, the survival rate for cancer patients has improved dramatically. "Nearly 36 percent fewer people are dying from cancer than they were in 1991," he said. "This progress is due to scientific research and clinical trials focused on prevention, early detection, and treatment."
Today, more people are living with cancer than ever before, thanks to these advancements. While the challenge of cancer remains, the outlook for patients is increasingly optimistic.
Conclusion
The variation in cancer diagnosis rates across the U.S. underscores the need for targeted public health efforts, particularly in regions with higher incidence. By addressing social determinants, improving access to care, and continuing to invest in research, the fight against cancer can become more effective and equitable.
Post a Comment for "Map reveals states with rising cancer rates"
Post a Comment