Doctors and Nurses Expose the Health "Lies" You Must Stop Believing
Common Health Myths and Misconceptions Revealed by Medical Professionals
Medical professionals often encounter a variety of health myths and misconceptions that patients believe to be true. These misunderstandings can lead to unnecessary anxiety, improper treatment, and even harm. Here are some of the most common myths and the truths behind them, as shared by doctors, nurses, and other healthcare workers.
1. Ambulances Don’t Guarantee Faster Care
Many people believe that calling an ambulance means they will be seen more quickly in the emergency department. However, this is not the case. If the issue could be addressed at an urgent care or primary care clinic, patients may end up waiting in the general waiting room until their condition is assessed. The severity of symptoms determines the order of care, not the method of arrival.
2. Not All Urine Abnormalities Mean Infection
A "dirty-looking" urine sample or an abnormal result on a urine test does not necessarily mean there is an infection. Similarly, a shadow on a chest X-ray or CT scan is not always pneumonia unless accompanied by symptoms like fever or difficulty breathing. Many skin conditions are also misdiagnosed as infections, leading to unnecessary antibiotic use.
3. High Blood Pressure Isn’t Always an Emergency
High blood pressure without other symptoms is not typically an emergency. Unless someone is experiencing severe symptoms such as chest pain, bleeding, or signs of a heart attack, blood pressure readings over 220/115 may require immediate attention. However, treating it too aggressively can lead to complications like fainting.
4. Over-the-Counter Medications Often Work
Emergency departments often prescribe over-the-counter medications for common issues like back or shoulder pain. Patients should try these options first before visiting the ER, as they may find relief without the high cost associated with emergency care.
5. Not Every Rash Is an Allergic Reaction
Rashes and hives can have various causes, including viral infections or environmental factors. Most rashes resolve on their own within a few days. Antihistamines like Zyrtec can help manage symptoms, and there’s no need to see an allergist immediately unless symptoms persist.
6. Avoiding the Internet for Diagnosis
Google is not a substitute for professional medical advice. While it can provide some information, it often leads to unnecessary worry. Patients should consult their primary care provider if symptoms persist for weeks or months instead of relying on online searches.
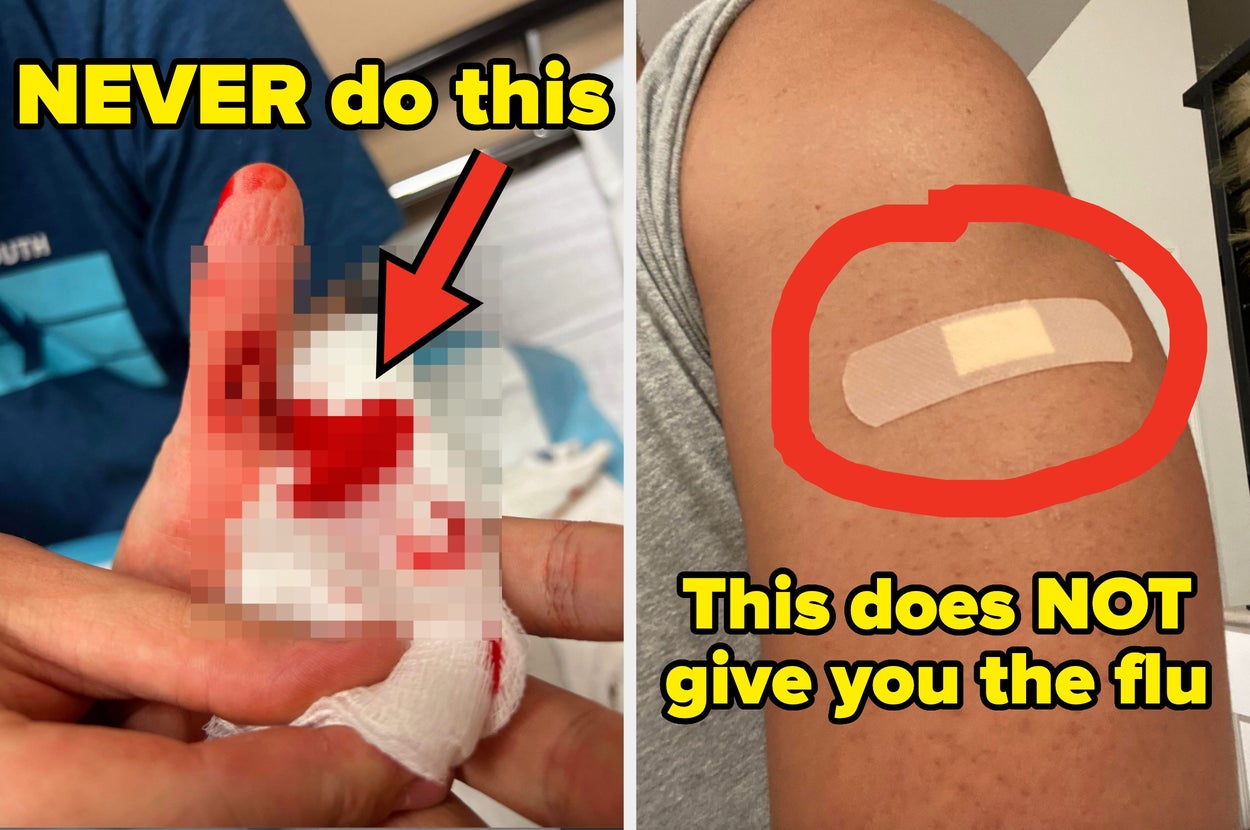
7. Wounds Need Moisture, Not Air
Contrary to popular belief, keeping wounds covered and moist promotes faster healing. Exposing a wound to air can actually slow down the recovery process. Covering the wound helps maintain the right environment for the body to heal itself.
8. Developmental Disorders Are Not Overdiagnosed
The increase in diagnoses of disorders like autism and ADHD is due to better research and understanding of how these conditions present. Historically, Black children were often misdiagnosed with Conduct Disorder instead of ADHD. As awareness grows, more accurate diagnoses are being made.
9. Healthcare Providers Can’t Control Costs
Doctors and nurses do not control drug prices, insurance coverage, or hospital bills. They often work within a flawed system that prioritizes profit over patient care. Despite this, many healthcare professionals strive to help patients navigate costs and ensure they receive necessary treatments.
10. Vaccine Side Effects Are Normal
Mild symptoms after a vaccine, such as a sore arm or slight fever, are a sign that the immune system is responding and building protection. These effects are common and not an indication of an allergic reaction. Inactivated vaccines cannot cause the disease they are designed to prevent.
11. Egg Allergies No Longer Prevent Flu Shots
Modern flu vaccines are produced without using eggs, making them safe for individuals with egg allergies. This is a common misconception that needs to be corrected.
12. Keeping Track of Medications Is Important
Patients should keep a list of their medications, allergies, and medical history in case they are unable to access digital records. Writing this information on a small card and carrying it in a wallet can be lifesaving in emergencies.
13. Peeing Doesn’t Mean Kidneys Are Healthy
The ability to urinate does not guarantee healthy kidney function. Some patients on dialysis still pee regularly but may not be eliminating toxins properly. Kidney health requires more than just the ability to urinate.
14. STI Testing Has Time Limits
Not all sexually transmitted infections show symptoms immediately. Some tests may not be reliable for up to two weeks after exposure. However, certain treatments, like HIV post-exposure prophylaxis, must be started within 72 hours of potential exposure.
15. Schizophrenia Does Not Mean Violence
People with schizophrenia are more likely to be victims of crime than perpetrators. Hallucinations can be caused by a range of conditions, including bipolar disorder, PTSD, and sleep deprivation. A diagnosis of schizophrenia does not equate to violence.
16. Food Allergies Are Different from Intolerances
Food allergies involve the immune system and can be life-threatening, while food intolerances are generally less severe. People should avoid claiming a food allergy unless they have a confirmed diagnosis, as it can affect others who truly need emergency care.
17. Healthcare Providers Face Challenges
Delays in appointments are often due to unforeseen circumstances, such as emergencies or administrative tasks. Doctors and nurses often sacrifice personal time to manage their responsibilities, so patience and kindness are appreciated.
18. Urgent Care Is Not for All Emergencies
Urgent care centers are not equipped to handle serious conditions like head injuries or chest pain. For these cases, patients should go to the emergency department for proper evaluation and treatment.
19. Detoxing Through Feet or Diets Is Unnecessary
The liver and kidneys naturally detoxify the body. There is no scientific evidence to support claims that essential oils, foot pads, or drastic diets can enhance this process.
20. Wearing a Seatbelt During Pregnancy Is Safe
Wearing a seatbelt during pregnancy is crucial for safety. It protects both the mother and the baby in the event of an accident. Proper placement of the seatbelt is important to ensure maximum protection.
These insights highlight the importance of seeking accurate medical information and understanding the realities behind common health myths. By educating themselves, patients can make informed decisions and improve their overall health outcomes.
Post a Comment for "Doctors and Nurses Expose the Health "Lies" You Must Stop Believing"
Post a Comment